Industry: Automotive, Off-Highway
Applocations: Powerpack/Powerplant
Challenge: In various industrial applications, air-to-liquid heat exchangers play a critical role in transferring heat from a hot fluid (often air) to a cooler liquid for temperature control. However, achieving optimal heat transfer performance can be challenging due to factors like:
- Limited space: Compact designs can restrict airflow and heat exchange efficiency.
- Fin geometry: Fin design significantly impacts air-to-liquid contact and heat transfer.
- Material selection: Choosing the right materials for fins and tubes balances heat conductivity with cost and weight.



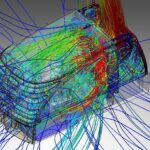
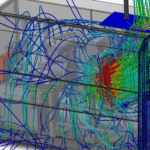
Solution: Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations provide a powerful tool for analyzing and optimizing air-to-liquid heat exchanger performance. This allows engineers to:
- Create virtual models: Develop detailed 3D models of the heat exchanger, including fin geometries, tube configurations, and surrounding components.
- Simulate airflow patterns: Replicate real-world airflow conditions, considering factors like air velocity, temperature, and turbulence.
- Analyze heat transfer: Evaluate the effectiveness of heat exchange between air and liquid, identifying areas of low efficiency or potential bottlenecks.
- Optimize heat exchanger design: Based on CFD results, refine fin geometry, tube layout, and material selection to maximize heat transfer and minimize pressure drop.
Benefits of CFD Simulations for Air-to-Liquid Heat Exchanger Optimization:
- Virtual Testing Environment: CFD eliminates the need for costly physical prototypes and testing, saving time and resources.
- Detailed Flow Insights: CFD provides a comprehensive understanding of airflow patterns and heat transfer phenomena within the heat exchanger, revealing areas for improvement.
- Predictive Capabilities: CFD can predict heat exchanger performance under varying operating conditions, allowing for proactive design optimization.
- Design Optimization: By analyzing the impact of design parameters on performance, engineers can optimize heat exchangers for enhanced heat transfer efficiency and reduced pressure drop.
Outcomes:
CFD simulations can significantly improve air-to-liquid heat exchanger design and performance by:
- Enhanced Heat Transfer: Optimized designs lead to increased heat exchange between air and liquid, ensuring efficient temperature control.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Improved heat transfer efficiency can lead to lower energy consumption for cooling or heating processes.
- Compact Design Optimization: CFD allows engineers to achieve optimal performance even with space constraints.
- Material Selection Optimization: CFD simulations help identify the most cost-effective materials that meet the required heat transfer characteristics.
Impact on Various Industries:
Implementing CFD simulations for air-to-liquid heat exchanger optimization offers advantages across several industries:
- Power Generation: Optimized heat exchangers in power plants enhance cooling efficiency of critical components, leading to increased power output and reduced operating costs.
- HVAC Systems: CFD simulations help design efficient air-to-liquid heat exchangers for air conditioners and heating systems, leading to improved building comfort and energy savings.
- Automotive: Optimized air-to-liquid heat exchangers in vehicles ensure efficient cooling of engines and radiators, enhancing performance and fuel economy.
- Chemical Processing: CFD plays a crucial role in designing heat exchangers for chemical reactions, ensuring optimal temperature control for efficient and safe operations.
Call to Action:
Are you facing challenges in optimizing the performance of your air-to-liquid heat exchangers? Our engineering team can help! We leverage advanced CFD simulation techniques to analyze and optimize heat exchanger designs, leading to:
- Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency
- Reduced Energy Consumption
- Compact and Cost-Effective Designs
- Improved System Reliability
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how CFD simulations can benefit your air-to-liquid heat exchanger design process.